internet
Internet
What is the Internet
TL;DR The internet is the physical layer that allows a device connect to each other via wire connection, wireless trough a local network or to the other side of the world with ISP and underwater cables.
The internet refers to a global network of interconnected computers and devices that enables the exchange of information and communication through a standardized set of protocols. It allows users to access a wide range of services, like the Web, IoT and many other inter-connected interactions between devices.
History
The development of the internet can be traced back to the 1960s, when the United States Department of Defense created ARPANET, a precursor to the modern internet. Since then, the internet has undergone significant advancements and has become more accessible to the general public, leading to the widespread adoption of its technology.
Main Components
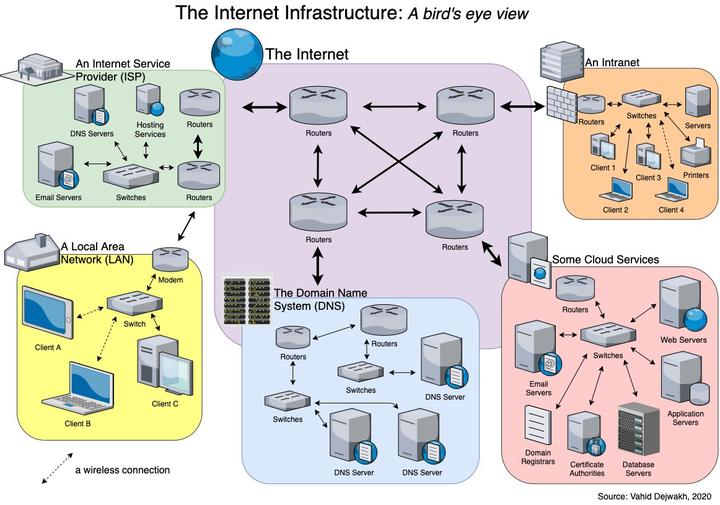
Internet Infrastructure
The internet relies on a complex infrastructure of physical networks, data centers, and servers to function. This includes undersea cables, satellite networks, and wireless connections.
Internet Protocols
Protocols, such as TCP/IP, govern the flow and exchange of data on the internet. These protocols are constantly evolving, and new ones are being developed to improve the efficiency and security of internet communication.
- TCP
- IP
- UDP
- HTTP
- HTTPS
- V1 / V2 / V3 (?)
- SMTP
- DNS
LAN
Internet Service Providers
Domain Name System
Cloud Services
Security and Challenges
Services
- Emails
- Web